General Election
November 4, 2025
It's a Presidential and Legislative Election Year!
YOUR VOTE COUNTS!
Yellow Pain's video "My Vote Don't Count" explores the perception of voter apathy and disenfranchisement within the context of government structure, shedding light on the significance of individual civic engagement. Through compelling storytelling and insightful commentary, the video prompts viewers to reconsider the impact of their votes and the role they play within the various levels of Maryland's state governance.
Yellow Pain's video "My Vote Don't Count" explores the perception of voter apathy and disenfranchisement within the context of government structure, shedding light on the significance of individual civic engagement. Through compelling storytelling and insightful commentary, the video prompts viewers to reconsider the impact of their votes and the role they play within the various levels of Maryland's state governance.
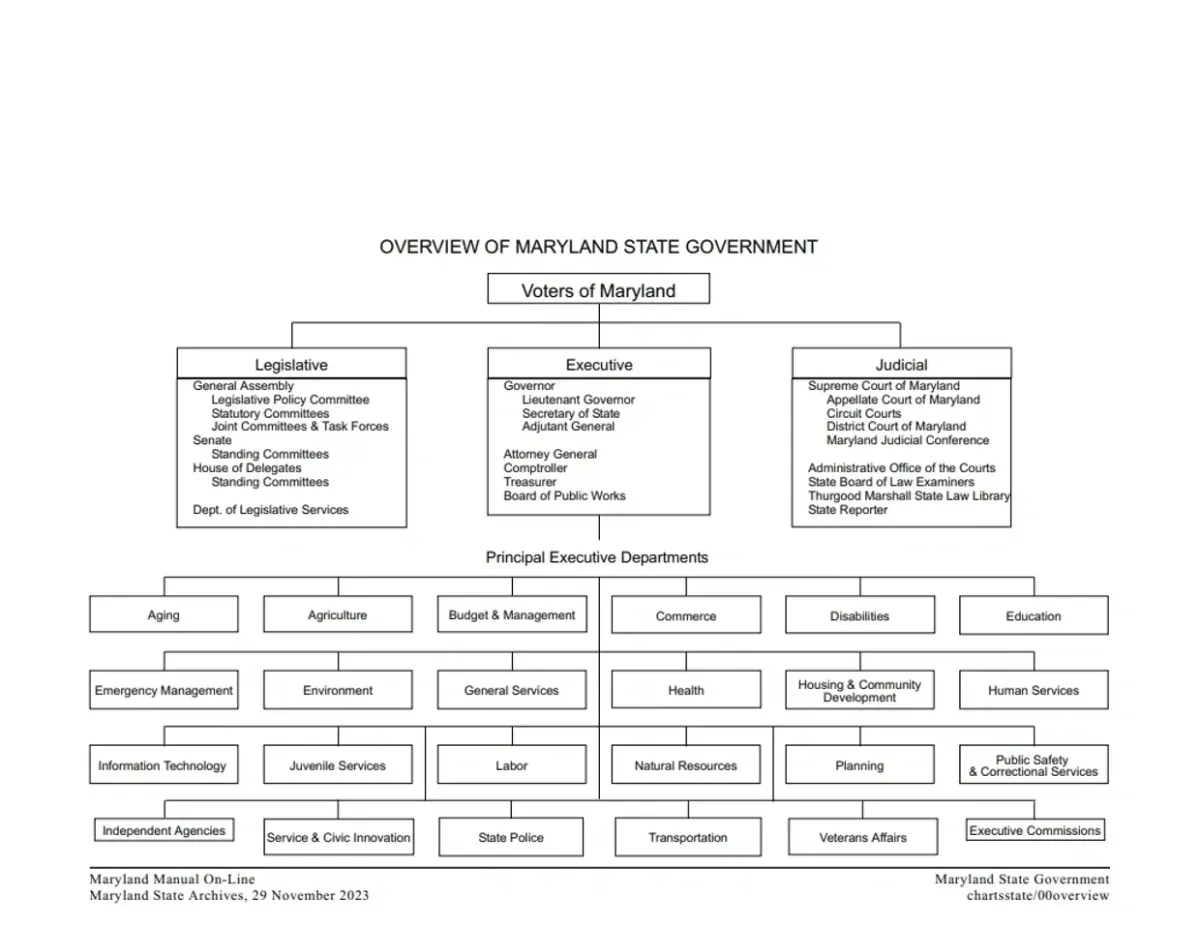
MARYLAND STATE GOVERNMENT
Voters, Executive Branch, Legislative Branch, Judicial Branch and Principle Executive Departments
Maryland's government consists of three branches: the Legislative Branch, which makes laws through the General Assembly; the Executive Branch, led by the Governor and responsible for implementing and enforcing laws; and the Judicial Branch, including the state courts, which interprets laws and ensures justice. Additionally, there are principal executive departments headed by appointed officials that oversee specific areas of governance.
MARYLAND STATE GOVERNMENT
Voters, Executive Branch, Legislative Branch, Judicial Branch and Principle Executive Departments
Maryland's government consists of three branches: the Legislative Branch, which makes laws through the General Assembly; the Executive Branch, led by the Governor and responsible for implementing and enforcing laws; and the Judicial Branch, including the state courts, which interprets laws and ensures justice. Additionally, there are principal executive departments headed by appointed officials that oversee specific areas of governance.